Management of Natural Resources
- The substances present is nature which is utilized by living organisms for their survival is said to be natural resources.
- Some natural resources like soil, air and water and various components are cycled over and over again in nature.
- To conserve our environment, natural resources like soil, water, forest, wildlife, coal, petroleum should be utilized in a proper manner and have to avoid their wastage.
- By the use of natural resources human manufacture a variety of modern conveniences.
- But we see that there are a limited natural resources but its exploitation is increasing day by day.
Why do we need to manage our resources?
- There are limited natural resources present on this earth.
- Due to rapid increase in population the natural resources are being utilized at an exponential rate.
- Human beings are not using the resources in eco-friendly way, as we see we are burning fossil fuels which harms environment.
- We also have to conserve our natural resources for our future generations.
- While using these resources, we have to reduce the damage caused to the environment.
- Garbage disposal should be safe.
3R’s to save our environment:

- The three ‘R’ are Reduce, Reuse, and Recycle.
- Reduce means to reduce the use of natural resources. As switch off the unnecessary bulb.
- Reuse means whatever the resources can be used again use it. As some plastic jars can be used again in keeping household things.
- Recycle means some of the resources which you have once used can be processed in industry to make it again usable. As newspaper after reading becomes waste to you but it is recycled to make a new page.
Forest and wildlife:

- Forest is regarded as the biodiversity hotspot.
Biodiversity:
- Biodiversity may be described as the variety of the lives on this earth in a particular region.
- It includes a wide variety of plants, animals, bacteria’s in a particular area.
- One of the main aims of conservation is to protect the diversity which we have inherited.
- Biodiversity forms the basis of the existence of human beings, by regulating climatic processes, decomposes wastes and recycles the nutrients, protects against flooding, maintains soil fertility and provide us natural resources like wood, textile and the most important food for our survival.
- When we lose diversity we will also lose the essential services provided by it.
Stakeholders:

Stakeholders are the peoples who are:
- The people who live in or around forests are dependent on forest produce for their life survival.
- There is a separate forest department assigned by government which owns the land and controls the resources from it.
- The industrialists who use various forest produce, but are not dependent on the forests in any one area. They take raw material for their factory.
- Some nature and wildlife enthusiasts who want to conserve nature in its pristine form works for conservation of forest.
Movements against forest exploitation:

- Amrita Devi Bishnoi is still remembered for her sacrifice to conserve wildlife.
- Amrita Devi Bishnoi along with her three daughters sacrificed their lives for the khejri tree which was being cut down and burnt to make the royal items of furniture.
- The Chipko Andolan: It was also called “hug the tree movement”. This movement started in a remotely located small village named Reni in Garhwal. It was a dispute between local villagers and the contractor who was given contract to cut down all the tree for their purpose which all the residents of the local village were dependent.
Sustainable management:
- Destruction of forests affects not just the availability of forest products, but also the quality of soil and the sources of water.
- The people associated with the forest should take care of it, Not just they should be only dependent on commercial use. They must ensure their sustainability.
Deforestation:

The cutting down of tree in a wide pace for commercial and many purposes are said to be deforestation. The main reasons behind deforestation are:
- Rapid industrialization
- Increasing population
- Tourism
- Development projects
Water:
- Water is the prime necessity of all the living organisms on this earth.
- Water is used primarily for drinking, irrigation and maintaining the close balance in nature.
Sources of water:
There are many sources of water to us, some of them are:
Rain:

- Rain is the main source of water in India.
- During the 3-4 months of monsoon all the rivers, lakes, ponds get filled with water thus fulfills the need of water.
- We make portable digs to store water to be used throughout the year.
Disadvantage of rain as a source of water:
- It can’t fulfil the needs of large and rapidly growing population.
- Rainwater is present in rivers and ponds but they are being polluted every day so it can’t be used for mankind.
Rivers:

- The water in the river either comes from the melting glaciers or from rain.
- To use water of river for various purpose such as hydroelectricity, irrigation etc. dams are constructed.
Dams:

- Dams store a large amount of water for irrigation and other purposes, Canal system carries the water from dams to different remote locations.
- Dams are also built to generate electricity. Electricity can be produced at a constant rate by the dams.
- From here water is supplied to the town and purified and is used for household purpose.
- The water is saved for the future use to fulfill them when the demand is high for electricity and water.
Disadvantage of dams:
- While constructing dams there arise social problems because they displace large number of peasants and tribals without adequate compensation or rehabilitation.
- They swallow up huge amounts of public money without the generation of proportionate benefits thus gives rise to Economic problems.
- It causes deforestation and the loss of biological diversity to a large extent thus cause environmental problems.
Water Harvesting:
As we hear every day that our groundwater level is decreasing day by day. So to maintain it we have to be aware of it. There are several methods maintain the water level. Most important among them is rainwater harvesting.
Rainwater harvesting:
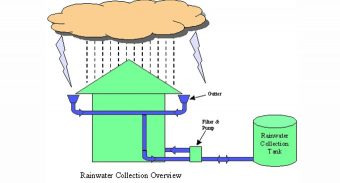
- Rainwater is collected in ponds and ditches when it falls on the earth.
- Stored water can be used in irrigation and related activities.
- This water also recharges the underground water level.
- It reduces cost of pumping underground groundwater.
COAL AND PETROLEUM:
- As we have discussed in sources of energy that coal and petroleum are fossil fuels as they are formed from the remains of living organisms.
- These fossil fuels are important sources of energy to us.
Uses of coal:
- As firewood.
- In making dyes, fertilizers, paper in industries.
- Thermal power plants make use of it.
- Coke is manufactured by coal.
Uses of petroleum:
- Used as fuel in vehicles, airplanes etc.
- As a raw material to produce fibres, detergents etc.
- Used as a lubricant
- Electricity is generated by using it.
The fossil fuels, coal and petroleum, will ultimately be exhausted. Because of this and because their combustion pollutes our environment, we need to use these resources judiciously.
To practice Question / Answer related to this chapter, Please visit Q/A Natural Resources






Be First to Comment